DUB Antibody Sampler Kit #8353
- Product Includes
- Related Products
| Product Includes | Quantity | Applications | Reactivity | MW(kDa) | Isotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phospho-CYLD (Ser418) Antibody #4500 | 20 µl | WB | H | 108 | Rabbit |
| STAMBP Antibody #5245 | 20 µl | WB, IP | H Mk | 50 | Rabbit |
| A20/TNFAIP3 (D13H3) Rabbit mAb #5630 | 20 µl | WB, IP | H M R Mk | 82 | Rabbit IgG |
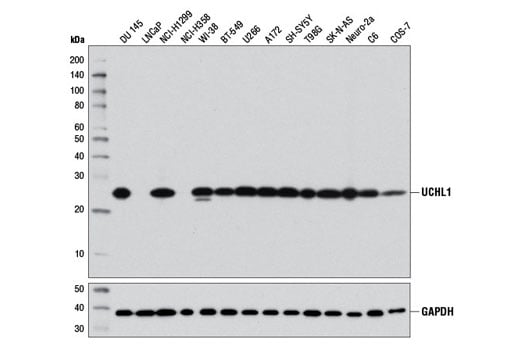
| UCHL1 (D3T2E) XP® Rabbit mAb #13179 | 20 µl | WB, IHC, IF, F | H M R Mk | 27 | Rabbit IgG |
| HAUSP (D17C6) XP® Rabbit mAb #4833 | 20 µl | WB, IP, IHC, IF | H M R Mk | 135, 140 | Rabbit IgG |
| USP9X Antibody #5751 | 20 µl | WB | H M R Mk Dg | 270 | Rabbit |
| CYLD (D1A10) Rabbit mAb #8462 | 20 µl | WB, IP | H M R Mk | 108 | Rabbit IgG |
| UCHL3 (D25E6) Rabbit mAb #8141 | 20 µl | WB | H M R | 27 | Rabbit IgG |
| USP10 (D7A5) Rabbit mAb #8501 | 20 µl | WB, IP, IF, eCLIP | H M R Mk | 110 | Rabbit IgG |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked Antibody #7074 | 100 µl | WB | Rab | Goat |
Product Information
Kit Usage Information
Protocols
- 4500: Western Blotting
- 4833: Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation (Magnetic), Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunofluorescence
- 5245: Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation (Magnetic)
- 5630: Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation (Magnetic)
- 5751: Western Blotting
- 7074: Western Blotting
- 8141: Western Blotting
- 8462: Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation (Agarose)
- 8501: Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation (Agarose), Immunofluorescence
- 13179: Western Blotting, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunofluorescence, Immunofluorescence, Flow
Product Description
The DUB Antibody Sampler Kit offers an economical means of evaluating the presence and status of selected DUB enzymes. This kit contains enough primary antibody to perform two western blot experiments per primary.
Background
Ubiquitinating enzymes (UBEs) catalyze protein ubiquitination, a reversible process countered by deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) action (1,2). CYLD deubiquitinase regulates inflammation and cell proliferation by down regulating NF-κB signaling through removal of ubiquitin chains from several NF-κB pathway proteins (3,4). Phosphorylation at Ser418 decreases CYLD deubiquitinase activity and is important for IKKε-driven transformation (5). STAM-binding protein (STAMBP or AMSH) is an endosomal DUB that preferentially displays ubiquitin isopeptidase activity toward K63-linked chains (6,7). The amino-terminus of A20 contains deubiquitinating activity for Lys63 branches, such as those found in TRAF6 and RIP, while the carboxyl-terminus contains ubiquitin ligase activity for Lys48 branches of the same substrates and leads to their degradation (8). Both enzymes have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases (9-11) and play a role in the regulation of neuronal development and spermatogenesis (10,13,14). UCHL1 binds monoubiquitin and UCHL3 shows affinity for both ubiquitin and NEDD8, a ubiquitin-like molecule (11,12). HAUSP can bind and deubiquitinate the p53 transcription factor and an associated regulator protein Mdm2, thereby stabilizing both proteins (15,16). HAUSP also modifies other ubiquitinated proteins such as members of the FoxO family of forkhead transcription factors and the mitotic stress checkpoint protein CHFR (17,18). USP10 appears to be regulated through both protein-protein interactions and phosphorylation. Interaction of USP10 with Ras-GAP SH3 domain binding protein (G3BP) inhibits its ability to disassemble ubiquitin chains (19). ATM-mediated phosphorylation at Thr42 and Ser337 stabilizes USP10, promoting redistribution from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where it functions in p53 deubiquitination, stabilization, and activation in response to genotoxic stress (20). USP9X possesses a well-conserved catalytic domain with cysteine peptidase activity, which allows for cleavage of ubiquitin and polyubiquitin conjugates. While USP9X expression has been shown to be critical for normal mammalian development (21-23), many of its substrates are only beginning to be elucidated.
- Nijman, S.M. et al. (2005) Cell 123, 773-86.
- Nalepa, G. et al. (2006) Nat Rev Drug Discov 5, 596-613.
- Regamey, A. et al. (2003) J Exp Med 198, 1959-64.
- Glittenberg, M. and Ligoxygakis, P. Fly (Austin) 1, 330-2.
- Hutti, J.E. et al. (2009) Mol Cell 34, 461-72.
- McCullough, J. et al. (2006) Curr Biol 16, 160-5.
- Kim, M.S. et al. (2006) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351, 612-8.
- Lin, S.C. et al. (2008) J Mol Biol 376, 526-40.
- Leroy, E. et al. (1998) Nature 395, 451-2.
- Kurihara, L.J. et al. (2001) Hum Mol Genet 10, 1963-70.
- Osaka, H. et al. (2003) Hum Mol Genet 12, 1945-58.
- Wada, H. et al. (1998) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251, 688-92.
- Sakurai, M. et al. (2006) J Cell Sci 119, 162-71.
- Kwon, J. (2007) Exp Anim 56, 71-7.
- Li, M. et al. (2002) Nature 416, 648-53.
- Brooks, C.L. et al. (2007) Oncogene 26, 7262-6.
- van der Horst, A. et al. (2006) Nat Cell Biol 8, 1064-73.
- Oh, Y.M. et al. (2007) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357, 615-9.
- Soncini, C. et al. (2001) Oncogene 20, 3869-79.
- Yuan, J. et al. (2010) Cell 140, 384-96.
- Pantaleon, M. et al. (2001) Mech Dev 109, 151-60.
- Noma, T. et al. (2002) Mech Dev 119 Suppl 1, S91-5.
- Xu, J. et al. (2005) J Neurosci Res 80, 47-55.
Pathways
Explore pathways related to this product.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.