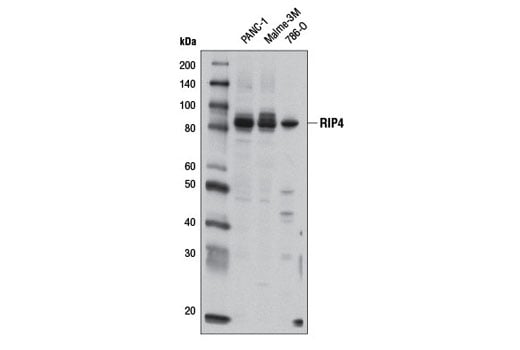
RIP4 Antibody #12636
Filter:
- WB
- IP
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 86 |
| SOURCE | Rabbit |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- IP-Immunoprecipitation
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
Storage
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/ml BSA and 50% glycerol. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
RIP4 Antibody recognizes endogenous levels of total RIP4 protein.
Species Reactivity:
Human
The antigen sequence used to produce this antibody shares 100% sequence homology with the species listed here, but reactivity has not been tested or confirmed to work by CST. Use of this product with these species is not covered under our Product Performance Guarantee.
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology:
Monkey
Source / Purification
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues near the carboxy terminus of human RIP4 protein. Antibodies are purified by protein A and peptide affinity chromatography.
Background
The receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine-threonine kinases (RIP, RIP2, RIP3, and RIP4) are important regulators of cellular stress that trigger pro-survival and inflammatory responses through the activation of NF-κB, as well as pro-apoptotic pathways (1). In addition to the kinase domain, RIP contains a death domain responsible for interaction with the death domain receptor Fas and recruitment to TNF-R1 through interaction with TRADD (2,3). RIP-deficient cells show a failure in TNF-mediated NF-κB activation, making the cells more sensitive to apoptosis (4,5). RIP also interacts with TNF-receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) and can recruit IKKs to the TNF-R1 signaling complex via interaction with NEMO, leading to IκB phosphorylation and degradation (6,7). Overexpression of RIP induces both NF-κB activation and apoptosis (2,3). Caspase-8-dependent cleavage of the RIP death domain can trigger the apoptotic activity of RIP (8).
Receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (RIP4, ANKRD3, DIK, PKK, or RIPK4) is a membrane-associated, ankyrin repeat-containing member of the RIP family first identified in HaCat cells (9,10). RIP4 has been shown to be involved in keratinocyte differentiation in vivo as well as wound repair (11-13). Studies indicate that siRNA knockdown of RIP4 in human xenografted tumor cells suppresses Wnt-dependent growth while over-expression of RIP4 in vitro stabilized β-catenin and lead to an increase in Wnt-dependent gene expression (14).
Receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 4 (RIP4, ANKRD3, DIK, PKK, or RIPK4) is a membrane-associated, ankyrin repeat-containing member of the RIP family first identified in HaCat cells (9,10). RIP4 has been shown to be involved in keratinocyte differentiation in vivo as well as wound repair (11-13). Studies indicate that siRNA knockdown of RIP4 in human xenografted tumor cells suppresses Wnt-dependent growth while over-expression of RIP4 in vitro stabilized β-catenin and lead to an increase in Wnt-dependent gene expression (14).
- Meylan, E. and Tschopp, J. (2005) Trends Biochem Sci 30, 151-9.
- Hsu, H. et al. (1996) Immunity 4, 387-96.
- Stanger, B.Z. et al. (1995) Cell 81, 513-23.
- Ting, A.T. et al. (1996) EMBO J 15, 6189-96.
- Kelliher, M.A. et al. (1998) Immunity 8, 297-303.
- Devin, A. et al. (2000) Immunity 12, 419-29.
- Zhang, S.Q. et al. (2000) Immunity 12, 301-11.
- Lin, Y. et al. (1999) Genes Dev 13, 2514-26.
- Bhr, C. et al. (2000) J Biol Chem 275, 36350-7.
- Chen, L. et al. (2001) J Biol Chem 276, 21737-44.
- Rountree, R.B. et al. (2010) J Invest Dermatol 130, 102-12.
- Adams, S. et al. (2007) J Invest Dermatol 127, 538-44.
- Holland, P. et al. (2002) Curr Biol 12, 1424-8.
- Huang, X. et al. (2013) Science 339, 1441-5.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.