R Recombinant
Recombinant: Superior lot-to-lot consistency, continuous supply, and animal-free manufacturing.
HDAC5 (D1J7V) Rabbit mAb #20458
Filter:
- WB
- IP
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R Mk |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 140 |
| Source/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- IP-Immunoprecipitation
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Mk-Monkey
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
Storage
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
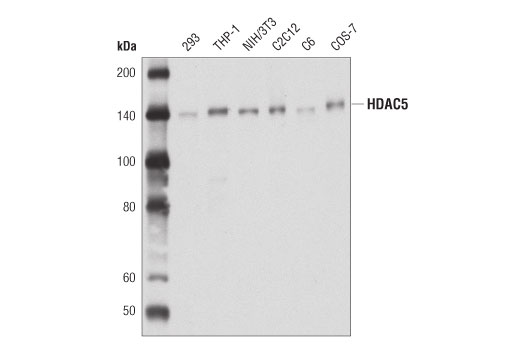
HDAC5 (D1J7V) Rabbit mAb recognizes endogenous levels of total HDAC5 protein. This antibody does not cross-react with other HDAC proteins, including HDAC4 and HDAC7.
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with recombinant protein surrounding Leu445 of human HDAC5 protein.
Background
Acetylation of the histone tail causes chromatin to adopt an "open" conformation, allowing increased accessibility of transcription factors to DNA. The identification of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and their large multiprotein complexes has yielded important insights into how these enzymes regulate transcription (1,2). HAT complexes interact with sequence-specific activator proteins to target specific genes. In addition to histones, HATs can acetylate nonhistone proteins, suggesting multiple roles for these enzymes (3). In contrast, histone deacetylation promotes a "closed" chromatin conformation and typically leads to repression of gene activity (4). Mammalian histone deacetylases can be divided into three classes on the basis of their similarity to various yeast deacetylases (5). Class I proteins (HDACs 1, 2, 3, and 8) are related to the yeast Rpd3-like proteins, those in class II (HDACs 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, and 10) are related to yeast Hda1-like proteins, and class III proteins are related to the yeast protein Sir2. Inhibitors of HDAC activity are now being explored as potential therapeutic cancer agents (6,7).
- Marmorstein, R. (2001) Cell Mol Life Sci 58, 693-703.
- Gregory, P.D. et al. (2001) Exp Cell Res 265, 195-202.
- Liu, Y. et al. (2000) Mol Cell Biol 20, 5540-53.
- Cress, W.D. and Seto, E. (2000) J Cell Physiol 184, 1-16.
- Gray, S.G. and Ekström, T.J. (2001) Exp Cell Res 262, 75-83.
- Thiagalingam, S. et al. (2003) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 983, 84-100.
- Vigushin, D.M. and Coombes, R.C. (2004) Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4, 205-18.
Pathways
Explore pathways related to this product.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
XP is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.