R Recombinant
Recombinant: Superior lot-to-lot consistency, continuous supply, and animal-free manufacturing.
CD44 v5 (C44Mab-3) Mouse mAb #36774
Filter:
- WB
- IHC
- F
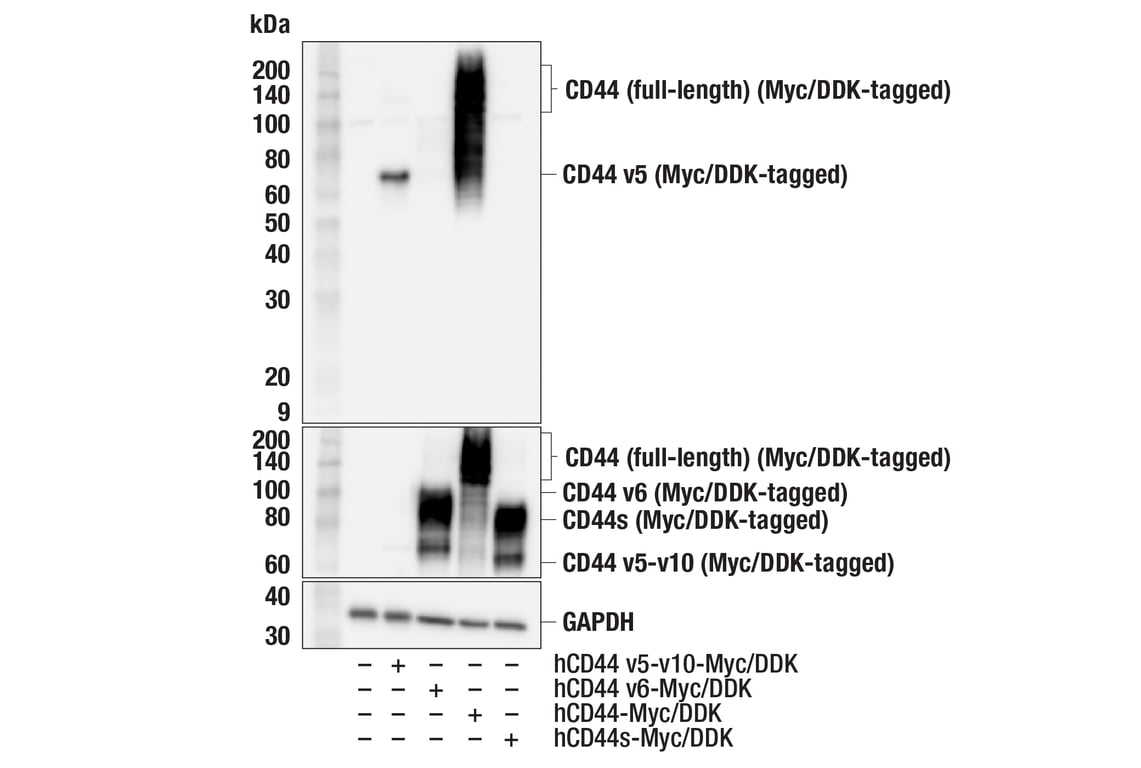
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 200-220 |
| Source/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 kappa |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- IHC-Immunohistochemistry
- F-Flow Cytometry
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:200 |
| Flow Cytometry (Live) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
Storage
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/mL BSA, 50% glycerol, and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
CD44 v5 (CD44Mab-3) Mouse mAb recognizes endogenous levels of total CD44 protein containing the variant v5 exon.
Species Reactivity:
Human
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with recombinant protein specific to the human CD44 variant v3-v10. This antigen has been further characterized as corresponding to residues surrounding His369 of human CD44 protein, within the CD44 variant v5 exon.
Background
CD44 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that mediates cell-cell and cell-matrix interaction through its affinity for hyaluronic acid (HA) and possibly through other parts of the extracellular matrix (ECM). CD44 is highly polymorphic, possesses a number of alternative splice variants and undergoes extensive post-translational modifications (1,2). Increased surface levels of CD44 are characteristic of T cell activation, and expression of the protein is upregulated during the inflammatory response. Research studies have shown that interactions between CD44 and HER2 are linked to an increase in ovarian carcinoma cell growth (1-3). CD44 interacts with ezrin, radixin, and moesin (ERM), linking the actin cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane and the ECM (4-6). CD44 is constitutively phosphorylated at Ser325 in resting cells. Activation of PKC results in phosphorylation of Ser291, dephosphorylation of Ser325, disassociation of ezrin from CD44, and directional motility (4).
Human CD44 consists of 19 exons, of which 10 are expressed in the standard isoform (CD44s) and all other isoforms. The nine variant exons (v2-v10) inserted between the constant regions via alternative splicing are the source of CD44 heterogeneity and can dramatically alter the cell-adhesion properties of CD44-expressing cells (7-10). Expression of CD44 isoforms containing exon v5 is associated with metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in breast cancer, pancreatic carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinomas, and intestinal stem cell-driven colorectal cancer (11-14). Among pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines, those that highly express CD44v, including CD44 v5, exhibit an epithelial or MET phenotype, express E-cadherin, and have an increased growth rate (9). Conversely, PDAC cells that highly express CD44s exhibit a mesenchymal phenotype, have high gemcitabine resistance, and co-express proteins associated with EMT transition, including vimentin and ZEB-1 (9). In vivo, PDAC cells have the ability to switch between expression of these CD44 isoforms in response to chemotherapy, demonstrating the importance of CD44-targeted therapies for treatment of some cancers (9).
Human CD44 consists of 19 exons, of which 10 are expressed in the standard isoform (CD44s) and all other isoforms. The nine variant exons (v2-v10) inserted between the constant regions via alternative splicing are the source of CD44 heterogeneity and can dramatically alter the cell-adhesion properties of CD44-expressing cells (7-10). Expression of CD44 isoforms containing exon v5 is associated with metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in breast cancer, pancreatic carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinomas, and intestinal stem cell-driven colorectal cancer (11-14). Among pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines, those that highly express CD44v, including CD44 v5, exhibit an epithelial or MET phenotype, express E-cadherin, and have an increased growth rate (9). Conversely, PDAC cells that highly express CD44s exhibit a mesenchymal phenotype, have high gemcitabine resistance, and co-express proteins associated with EMT transition, including vimentin and ZEB-1 (9). In vivo, PDAC cells have the ability to switch between expression of these CD44 isoforms in response to chemotherapy, demonstrating the importance of CD44-targeted therapies for treatment of some cancers (9).
- Goodison, S. et al. (1999) Mol. Pathol. 52, 189-196.
- Cichy, J. and Puré, E. (2003) J. Cell Biol. 161, 839-843.
- Bourguignon, L.Y. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 27913-27918.
- Legg, J.W. et al. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 399-407.
- Yonemura, S. et al. (1998) J. Cell Biol. 140, 885-895.
- Tsukita, S. et al. (1994) J. Cell Biol. 126, 391-401.
- Kudo, Y. et al. (2023) Antibodies (Basel) 12, 31. doi: 10.3390/antib12020031.
- Chen, C. et al. (2018) J Hematol Oncol 11, 64.
- Zhao, S. et al. (2016) Clin Cancer Res 22, 5592-5604.
- Rudzki, Z. and Jothy, S. (1997) Mol Pathol 50, 57-71.
- Kaufmann, M. et al. (1995) Lancet 345, 615-9.
- Piselli, P. et al. (2000) Anticancer Res 20, 825-31.
- Tran, T.A. et al. (1997) Hum Pathol 28, 809-14.
- Zeilstra, J. et al. (2014) Oncogene 33, 665-70.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.