R Recombinant
Recombinant: Superior lot-to-lot consistency, continuous supply, and animal-free manufacturing.
Atg13 (D4P1K) Rabbit mAb (BSA and Azide Free) #41634
Filter:
- WB
- ELISA
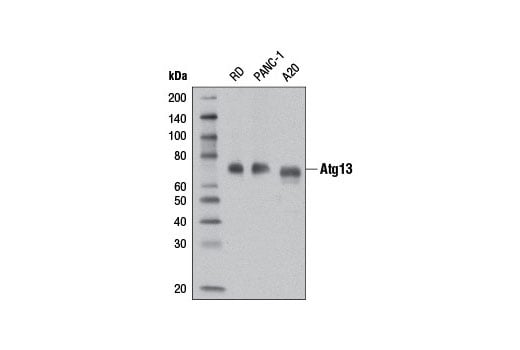
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 72 |
| Source/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- ELISA-ELISA
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
This product is the carrier free version of product #13273. All data were generated using the same antibody clone in the standard formulation which contains BSA and glycerol.
This formulation is ideal for use with technologies requiring specialized or custom antibody labeling, including fluorophores, metals, lanthanides, and oligonucleotides. It is not recommended for ChIP, ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN or CUT&Tag assays. If you require a carrier free formulation for chromatin profiling, please contact us. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
BSA and Azide Free antibodies are quality control tested by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine antibody integrity.
This formulation is ideal for use with technologies requiring specialized or custom antibody labeling, including fluorophores, metals, lanthanides, and oligonucleotides. It is not recommended for ChIP, ChIP-seq, CUT&RUN or CUT&Tag assays. If you require a carrier free formulation for chromatin profiling, please contact us. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
BSA and Azide Free antibodies are quality control tested by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to determine antibody integrity.
Formulation
Supplied in 1X PBS (10 mM Na2HPO4, 3 mM KCl, 2 mM KH2PO4, and 140 mM NaCl (pH 7.8)). BSA and Azide Free.
For standard formulation of this product see product #13273
For standard formulation of this product see product #13273
Storage
Store at -20°C. This product will freeze at -20°C so it is recommended to aliquot into single-use vials to avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles. A slight precipitate may be present and can be dissolved by gently vortexing. This will not interfere with antibody performance.
Specificity / Sensitivity
Atg13 (D4P1K) Rabbit mAb (BSA and Azide Free) recognizes endogenous levels of total Atg13 protein.
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Asp462 of human Atg13 protein.
Background
Autophagy is a catabolic process for the autophagosomic-lysosomal degradation of bulk cytoplasmic contents (1,2). Autophagy is generally activated by conditions of nutrient deprivation but has also been associated with a number of physiological processes including development, differentiation, neurodegeneration, infection, and cancer (3). The molecular machinery of autophagy was largely discovered in yeast and referred to as autophagy-related (Atg) genes.
Atg13/Apg13 was originally identified in yeast as a constitutively expressed protein that was genetically linked to Atg1/Apg1, a protein kinase required for autophagy (4). Overexpression of Atg1 suppresses the defects in autophagy observed in Atg13 mutants (4). Autophagy requires a direct association between Atg1 and Atg13, and is inhibited by TOR-dependent phosphorylation of Atg13 under high-nutrient conditions (5). Similarly, mammalian Atg13 forms a complex with the Atg1 homologues ULK1/2, along with FIP200, which localizes to autophagic isolation membranes and regulates autophagosome biogenesis (6-8). mTOR phosphorylates both Atg13 and ULK1, suppressing ULK1 kinase activity and autophagy (7-9). ULK1 can directly phosphorylate Atg13 at a yet unidentified site, presumably to promote autophagy (7,8). Additional studies suggest that Atg13 and FIP200 can function independently of ULK1 and ULK2 to induce autophagy through an unknown mechanism (10).
Atg13/Apg13 was originally identified in yeast as a constitutively expressed protein that was genetically linked to Atg1/Apg1, a protein kinase required for autophagy (4). Overexpression of Atg1 suppresses the defects in autophagy observed in Atg13 mutants (4). Autophagy requires a direct association between Atg1 and Atg13, and is inhibited by TOR-dependent phosphorylation of Atg13 under high-nutrient conditions (5). Similarly, mammalian Atg13 forms a complex with the Atg1 homologues ULK1/2, along with FIP200, which localizes to autophagic isolation membranes and regulates autophagosome biogenesis (6-8). mTOR phosphorylates both Atg13 and ULK1, suppressing ULK1 kinase activity and autophagy (7-9). ULK1 can directly phosphorylate Atg13 at a yet unidentified site, presumably to promote autophagy (7,8). Additional studies suggest that Atg13 and FIP200 can function independently of ULK1 and ULK2 to induce autophagy through an unknown mechanism (10).
- Reggiori, F. and Klionsky, D.J. (2002) Eukaryot Cell 1, 11-21.
- Codogno, P. and Meijer, A.J. (2005) Cell Death Differ 12 Suppl 2, 1509-18.
- Levine, B. and Yuan, J. (2005) J Clin Invest 115, 2679-88.
- Funakoshi, T. et al. (1997) Gene 192, 207-13.
- Kamada, Y. et al. (2000) J Cell Biol 150, 1507-13.
- Ganley, I.G. et al. (2009) J Biol Chem 284, 12297-305.
- Hosokawa, N. et al. (2009) Mol Biol Cell 20, 1981-91.
- Jung, C.H. et al. (2009) Mol Biol Cell 20, 1992-2003.
- Kim, J. et al. (2011) Nat Cell Biol 13, 132-41.
- Alers, S. et al. (2011) Autophagy 7, 1423-33.
Pathways
Explore pathways related to this product.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
SignalSilence is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
XP is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.