c-Jun Control Cell Extracts #9263
Filter:
- WB
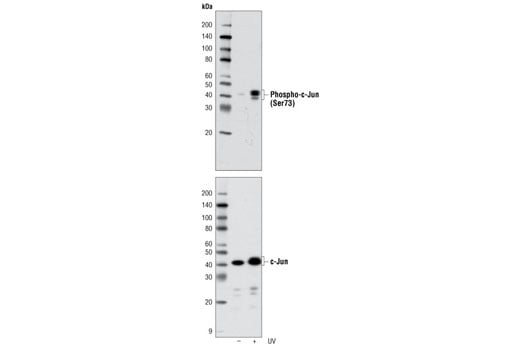
Western blot analysis of c-Jun Control Cell Extracts using Phospho-c-Jun (Ser73) (D47G9) XP® Rabbit mAb #3270 (upper) and c-Jun (60A8) Rabbit mAb #9165 (lower).
- Product Includes
- Related Products
| Product Includes | Quantity |
|---|---|
| c-Jun Control Cell Extracts (3T3 untreated) #92953 | 150 µl |
| c-Jun Control Cell Extracts (3T3 +UV) #31928 | 150 µl |
Product Information
Product Usage Information
Boil for 3 minutes prior to use. Load 15 µl of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated c-Jun Control Cell Extracts per lane.
Storage
Supplied in SDS Sample Buffer: 62.5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8 at 25°C), 2% w/v SDS, 10% glycerol, 50 mM DTT, 0.01% w/v phenol red or bromophenol blue. Store at –20°C or at –80°C for long term storage.
Product Description
Nonphosphorylated c-Jun Control Cell Extracts: Total cell extracts from NIH/3T3 cells, serve as a negative control. Supplied in SDS Sample Buffer.
Phosphorylated c-Jun Control Cell Extracts: Total cell extracts from NIH/3T3 cells, treated with 50 mJ UV light and a 30 minute recovery, serve as a positive control. Supplied in SDS Sample Buffer.
Phosphorylated c-Jun Control Cell Extracts: Total cell extracts from NIH/3T3 cells, treated with 50 mJ UV light and a 30 minute recovery, serve as a positive control. Supplied in SDS Sample Buffer.
Background
c-Jun is a member of the Jun family containing c-Jun, JunB, and JunD, and is a component of the transcription factor activator protein-1 (AP-1). AP-1 is composed of dimers of Fos, Jun, and ATF family members and binds to and activates transcription at TRE/AP-1 elements (reviewed in 1). Extracellular signals, including growth factors, chemokines, and stress, activate AP-1-dependent transcription. The transcriptional activity of c-Jun is regulated by phosphorylation at Ser63 and Ser73 through SAPK/JNK (reviewed in 2). Knockout studies in mice have shown that c-Jun is essential for embryogenesis (3), and subsequent studies have demonstrated roles for c-Jun in various tissues and developmental processes, including axon regeneration (4), liver regeneration (5), and T cell development (6). AP-1 regulated genes exert diverse biological functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as transformation, invasion and metastasis, depending on cell type and context (7-9). Other target genes regulate survival, as well as hypoxia and angiogenesis (8,10). Research studies have implicated c-Jun as a promising therapeutic target for cancer, vascular remodeling, acute inflammation, and rheumatoid arthritis (11,12).
- Jochum, W. et al. (2001) Oncogene 20, 2401-12.
- Davis, R.J. (2000) Cell 103, 239-52.
- Hilberg, F. et al. (1993) Nature 365, 179-81.
- Raivich, G. et al. (2004) Neuron 43, 57-67.
- Behrens, A. et al. (2002) EMBO J 21, 1782-90.
- Riera-Sans, L. and Behrens, A. (2007) J Immunol 178, 5690-700.
- Leppä, S. and Bohmann, D. (1999) Oncogene 18, 6158-62.
- Shaulian, E. and Karin, M. (2002) Nat Cell Biol 4, E131-6.
- Weiss, C. and Bohmann, D. (2004) Cell Cycle 3, 111-3.
- Karamouzis, M.V. et al. (2007) Mol Cancer Res 5, 109-20.
- Kim, S. and Iwao, H. (2003) J Pharmacol Sci 91, 177-81.
- Dass, C.R. and Choong, P.F. (2008) Pharmazie 63, 411-4.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.

