SimpleChIP® Human TGFBR2 Promoter Primers #39833
Filter:
- ChIP
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H |
Application Key:
- ChIP-Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Description
SimpleChIP® Human TGFBR2 Promoter Primers contain a mix of forward and reverse PCR primers that are specific to a region of the human TGF-beta receptor type-2 promoter. These primers can be used to amplify DNA that has been isolated using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Primers have been optimized for use in SYBR® Green quantitative real-time PCR and have been tested in conjunction with SimpleChIP® Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kits #9004 and #9005 and ChIP-validated antibodies from Cell Signaling Technology®.
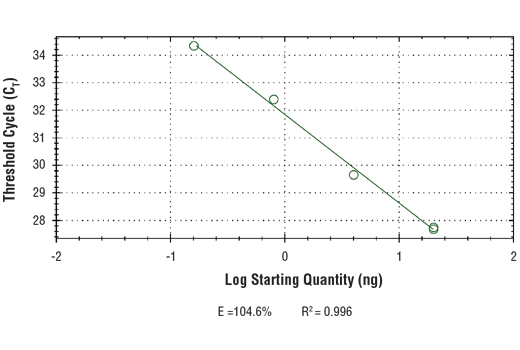
| Endotoxin | 1. Label the appropriate number of PCR tubes or PCR plates compatible with the model of real-time PCR machine to be used. PCR reactions should be performed in duplicate and should include a tube with no DNA to control for contamination, and a serial dilution of a 2% total input chromatin DNA (undiluted, 1:5, 1:25, 1:125), which is used to create a standard curve and determine amplification efficiency.2. Add 2 μl of the appropriate ChIP DNA sample to each tube or well of the PCR plate.3. Prepare a master PCR reaction mix as described below. Add enough reagents for two extra reactions to account for loss of volume. Add 18 μl of the master PCR reaction mix to each PCR reaction tube or well of the PCR plate.Reagent Volume for 1 PCR Reaction (20 μl)Nuclease-free H2O 6 μl5 μM SimpleChIP® Primers 2 μl2X SYBR® Green Reaction Mix 10 μl4. Start the following PCR reaction program:a. Initial Denaturation: 95°C for 3 min.b. Denaturation: 95°C for 15 sec.c. Anneal and Extension: Primer-specific temp. for 60 sec.d. Repeat steps b and c for a total of 40 cycles.5. Analyze quantitative PCR results using software provided with the real-time PCR machine. |
Storage
Supplied in nuclease-free water at a concentration of 5 µM (each primer is at a final concentration of 5 µM). Store at -20°C.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human
Background
The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is a powerful and versatile technique used for probing protein-DNA interactions within the natural chromatin context of the cell (1,2). This assay can be used to either identify multiple proteins associated with a specific region of the genome or to identify the many regions of the genome bound by a particular protein (3-6). ChIP can be used to determine the specific order of recruitment of various proteins to a gene promoter or to "measure" the relative amount of a particular histone modification across an entire gene locus (3,4). In addition to histone proteins, the ChIP assay can be used to analyze binding of transcription factors and co-factors, DNA replication factors, and DNA repair proteins. When performing the ChIP assay, cells are first fixed with formaldehyde, a reversible protein-DNA cross-linking agent that "preserves" the protein-DNA interactions occurring in the cell (1,2). Cells are lysed and chromatin is harvested and fragmented using either sonication or enzymatic digestion. Fragmented chromatin is then immunoprecipitated with antibodies specific to a particular protein or histone modification. Any DNA sequences that are associated with the protein or histone modification of interest will co-precipitate as part of the cross-linked chromatin complex and the relative amount of that DNA sequence will be enriched by the immunoselection process. After immunoprecipitation, the protein-DNA cross-links are reversed and the DNA is purified. Standard PCR or quantitative real-time PCR are often used to measure the amount of enrichment of a particular DNA sequence by a protein-specific immunoprecipitation (1,2). Alternatively, the ChIP assay can be combined with genomic tiling micro-array (ChIP on chip) techniques, high throughput sequencing (ChIP-Seq), or cloning strategies, all of which allow for genome-wide analysis of protein-DNA interactions and histone modifications (5-8). SimpleChIP® primers have been optimized for amplification of ChIP-isolated DNA using real-time quantitative PCR and provide important positive and negative controls that can be used to confirm a successful ChIP experiment.
- Orlando, V. (2000) Trends Biochem Sci 25, 99-104.
- Kuo, M.H. and Allis, C.D. (1999) Methods 19, 425-33.
- Agalioti, T. et al. (2000) Cell 103, 667-78.
- Soutoglou, E. and Talianidis, I. (2002) Science 295, 1901-4.
- Mikkelsen, T.S. et al. (2007) Nature 448, 553-60.
- Lee, T.I. et al. (2006) Cell 125, 301-13.
- Weinmann, A.S. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 37-47.
- Wells, J. and Farnham, P.J. (2002) Methods 26, 48-56.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
SimpleChIP is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.