Pepstatin A #98806
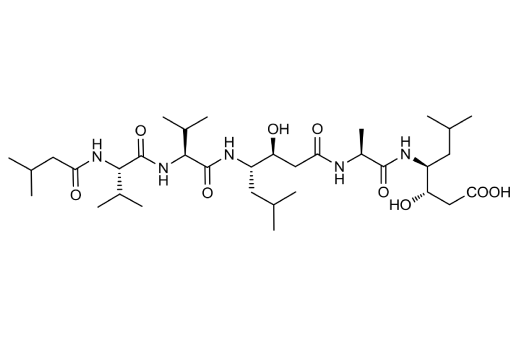
Chemical structure of Pepstatin A.
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
Pepstatin A is supplied as a lyophilized powder. For a 10 mM stock, reconstitute 5 mg of powder in 0.73 mL of DMSO. Working concentrations and length of treatment can vary depending on the desired effect.
Storage
Store lyophilized at -20ºC, desiccated. In lyophilized form, the chemical is stable for 24 months. Once in solution, store at -20ºC and use within 2 months to prevent loss of potency. Aliquot to avoid multiple freeze/thaw cycles.
Product Description
| Molecular Weight | 685.9 g/mol |
| Purity | >98% |
| Molecular Formula | C34H63N5O9 |
| CAS | 26305-03-3 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO at 5 mg/mL or ethanol at 1 mg/mL. |
Background
Pepstatin A is a low molecular weight inhibitor of aspartyl proteases, including pepsin, renin, cathepsin D and cathepsin E (1). Cathepsin D is a ubiquitously expressed lysosomal aspartyl protease involved in the normal degradation of proteins; dysregulation of cathepsin D plays a role in neuronal degradation and malignant transformation. Cathespin D is highly expressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Pepstatin A treatment induced apoptosis and autophagy while reducing the proliferation, invasion, and migration of TNBC cells (2). Increased expression and leakage of lysosomal cathepsin D is associated with cardiomyocyte death related to hyperglycemia. Treatment with Pepstatin A markedly diminished high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte death (3). Pepstatin A treatment of osteoclast cells suppressed receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced differentiation to mononuclear osteoclast cells by blocking NFATc1 expression and inhibiting ERK signaling (4). Pepstatin A also inhibits human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease (5). Pepstatin A treatment of HIV-infected H9 cells decreased the level of HIV core antigen in the culture medium (6).
- Umezawa, H. et al. (1970) J Antibiot (Tokyo) 23, 259-62.
- Zóia, M.A.P. et al. (2019) Int J Mol Sci 20, 1337. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061337.
- Kobayashi, S. et al. (2020) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 523, 239-245.
- Yoshida, H. et al. (2006) J Biochem 139, 583-90.
- Sarubbi, E. et al. (1993) FEBS Lett 319, 253-6.
- von der Helm, K. et al. (1989) FEBS Lett 247, 349-52.
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.

