R Recombinant
Recombinant: Superior lot-to-lot consistency, continuous supply, and animal-free manufacturing.
Neurofilament-H (E7Z7G) Rabbit mAb #30564
Filter:
- WB
- IP
- IHC
- IF
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 180-220 |
| Source/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- IP-Immunoprecipitation
- IHC-Immunohistochemistry
- IF-Immunofluorescence
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:100 |
| IHC Leica Bond | 1:100 - 1:400 |
| Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) | 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (Frozen) | 1:100 - 1:400 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:1600 - 1:6400 |
Storage
Supplied in 10 mM sodium HEPES (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 100 µg/mL BSA, 50% glycerol, and less than 0.02% sodium azide. Store at –20°C. Do not aliquot the antibody.
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #40459.
For a carrier free (BSA and azide free) version of this product see product #40459.
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
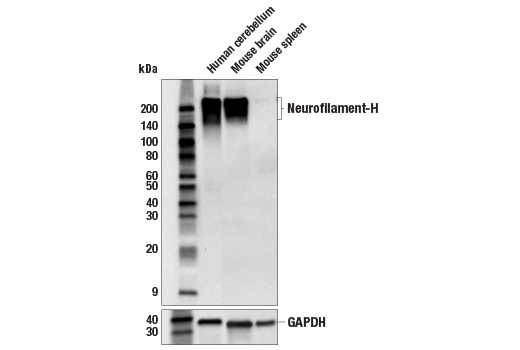
Neurofilament-H (E7Z7G) Rabbit mAb recognizes endogenous levels of total Neurofilament-H protein. Non-specific staining was observed in some tumor and normal epithelium by immunohistochemistry.
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Lys996 of human Neurofilament-H protein.
Background
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: actin microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Neurofilaments are the major intermediate filaments found in neurons and consist of light (NFL), medium (NFM), and heavy (NFH) subunits (1). Similar in structure to other intermediate filament proteins, neurofilaments have a globular amino-terminal head, a central α-helical rod domain, and a carboxy-terminal tail. A heterotetrameric unit (NFL-NFM and NFL-NFH) forms a protofilament, with eight protofilaments comprising the typical 10 nm intermediate filament (2). While neurofilaments are critical for radial axon growth and determine axon caliber, microtubules are involved in axon elongation. PKA phosphorylates the head domain of NFL and NFM to inhibit neurofilament assembly (3,4). Research studies have shown neurofilament accumulations in many human neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease (in Lewy bodies along with α-synuclein), Alzheimer's disease, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) (1).
限制使用
除非 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书行明确同意,否书以下条款适用于 CST、其关书方或分书商提供的书品。 任何书充本条款或与本条款不同的客书条款和条件,除非书 CST 的合法授书代表以书面形式书独接受, 否书均被拒书,并且无效。
专品专有“专供研究使用”的专专或专似的专专声明, 且未专得美国食品和专品管理局或其他外国或国内专管机专专专任何用途的批准、准专或专可。客专不得将任何专品用于任何专断或治专目的, 或以任何不符合专专声明的方式使用专品。CST 专售或专可的专品提供专作专最专用专的客专,且专用于研专用途。将专品用于专断、专防或治专目的, 或专专售(专独或作专专成)或其他商专目的而专专专品,均需要 CST 的专独专可。客专:(a) 不得专独或与其他材料专合向任何第三方出售、专可、 出借、捐专或以其他方式专专或提供任何专品,或使用专品制造任何商专专品,(b) 不得复制、修改、逆向工程、反专专、 反专专专品或以其他方式专专专专专品的基专专专或技专,或使用专品开专任何与 CST 的专品或服专专争的专品或服专, (c) 不得更改或专除专品上的任何商专、商品名称、徽专、专利或版专声明或专专,(d) 只能根据 CST 的专品专售条款和任何适用文档使用专品, (e) 专遵守客专与专品一起使用的任何第三方专品或服专的任何专可、服专条款或专似专专
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit our
Trademark Information page.